Requirement
AC.L2-3.1.7 – Prevent non-privileged users from executing privileged functions and capture the execution of such functions in audit logs. This control comes from NIST SP 800-171 REV.2 / CMMC 2.0 Level 2.
Understanding the Requirement
This control requires you to define what “privileged functions” are in your environment, clearly separate privileged users from non-privileged users, technically prevent non-privileged users from performing privileged actions, and log all executions of privileged functions. Privileged functions include actions like changing system settings, installing software, modifying security configurations, and altering audit logs. By limiting who can perform these actions and auditing their use, you reduce risk and can detect policy violations or malicious activity.
Policies and Procedures Needed
Document a least-privilege access policy that defines privileged functions, admin roles, and non-privileged users; a request-and-approval process for assigning and activating admin roles; and procedures for onboarding/offboarding, break-glass accounts, and service account governance. Include standards for removing local administrator rights, approving software installations and configuration changes, performing periodic access reviews (especially for admin roles and sensitive groups), and retaining/auditing logs for privileged activity. Define exceptions and emergency elevation steps with time limits, approval, and post-incident review.
Technical Implementation in Microsoft 365
- Define and assign admin roles in Entra ID (Azure AD) using least privilege. Use Entra ID Privileged Identity Management (PIM) to make admin role assignments eligible, require MFA, justification, and approval for activation, set short activation durations, and enable notifications for role activations.
- Remove local administrator rights from users with Intune: deploy a device configuration profile (Settings Catalog > Local user group membership) to ensure only designated admin groups are in the local Administrators group. Use Intune device restriction policies to block users from installing apps and accessing the Microsoft Store, and require elevation via approved admins when software changes are needed.
- Control access to privileged portals with Conditional Access. Create policies that require MFA, compliant devices, and trusted locations for admin role users, and block legacy authentication. Apply stricter policies to high-impact roles (Global Administrator, Privileged Role Administrator).
- Reduce who can perform tenant-level privileged actions in Entra ID: in User settings, restrict who can register applications and consent to apps; limit who can join devices to the tenant; and scope admin permissions with Administrative Units where appropriate.
- Continuously review privileged access with Entra ID Access Reviews. Schedule recurring (e.g., quarterly) reviews for admin roles and sensitive security groups, require reviewers to attest to ongoing need, and configure automatic removal for non-responders.
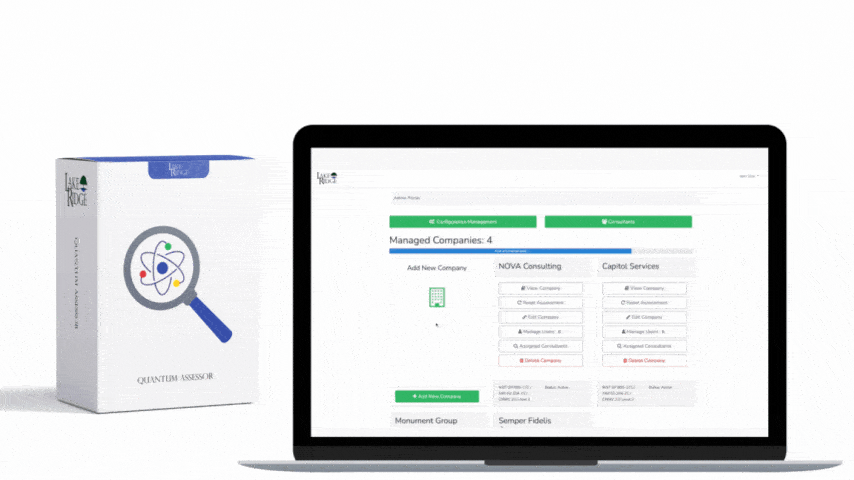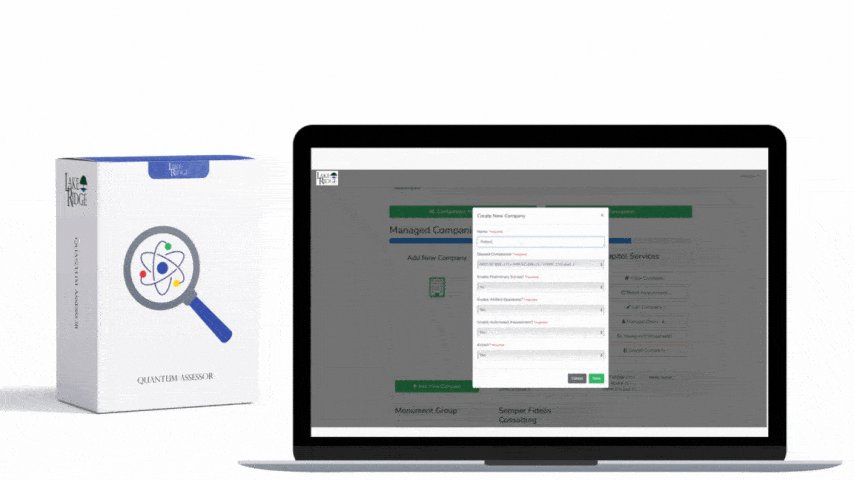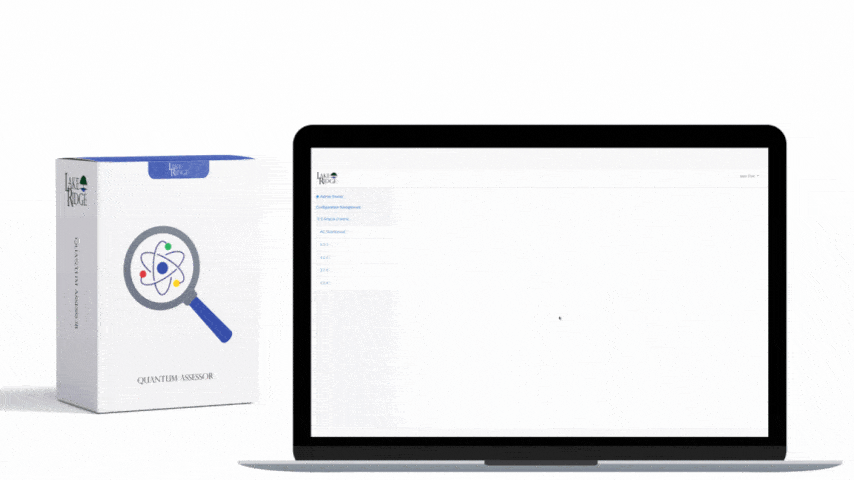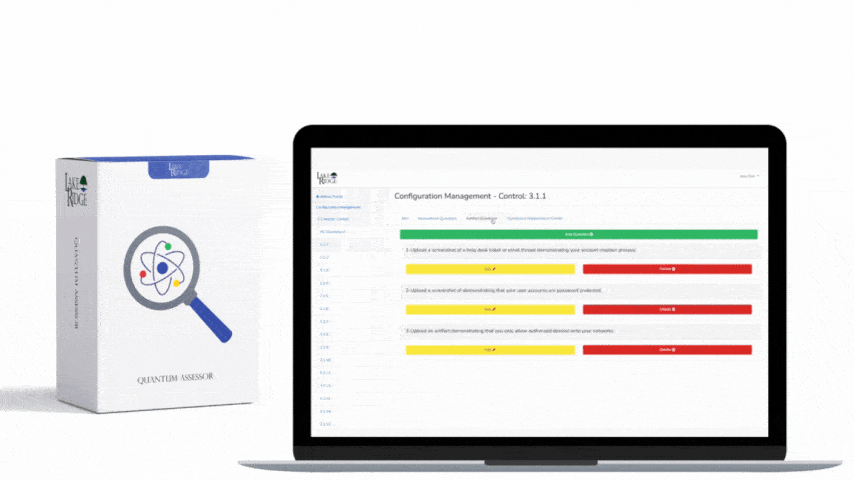
- Capture and monitor privileged activity with Microsoft 365 audit logs. Ensure Microsoft Purview Audit (Standard) is enabled, and verify Entra ID audit/sign-in logs and Microsoft 365 service audit logs are retained per policy. Create alert policies for high-risk events (e.g., role assignments, Conditional Access changes, mailbox permission changes), and regularly review admin activity reports.
- Detect risky privileged usage with Entra ID Identity Protection. Configure sign-in risk and user risk policies (at minimum for admin role users) to require MFA, force password reset, or block sign-ins when risk is high.
Example in a Small or Medium Business
A 120-person professional services firm standardizes on Microsoft 365 Business Premium and enrolls all devices in Intune. The IT lead defines privileged functions: installing software, changing security settings, modifying Conditional Access, and assigning licenses or roles. They remove local admin rights from all users via Intune’s Local user group membership policy and block app installs through device restrictions, requiring help desk to deploy applications. Admin roles in Entra ID are reworked to least privilege, and all admin assignments become eligible through PIM, with approval, justification, and a one-hour activation window. Conditional Access enforces MFA and compliant devices for any user in an active admin role and blocks legacy authentication. The firm enables Microsoft Purview Audit and configures alert policies for events like role assignment changes, new Conditional Access policies, and mailbox permission changes; the IT lead reviews admin activity weekly. Quarterly, an Entra ID Access Review runs for all privileged roles and security groups, automatically removing access if reviewers don’t confirm continued need. When a project manager requests temporary software that needs elevated rights, help desk deploys it via Intune, preserving the user’s standard role and ensuring the action is logged.
Summary
By defining privileged functions, separating privileged from non-privileged users, and enforcing least privilege with Entra ID, PIM, Intune, Conditional Access, Access Reviews, Identity Protection, and Microsoft 365 audit logs, SMBs can both prevent unauthorized privileged actions and capture all legitimate executions in audit trails. These policy and technical measures work together to minimize risk, ensure only approved administrators can perform sensitive tasks, and provide the visibility needed to investigate and prove compliance with AC.L2-3.1.7.