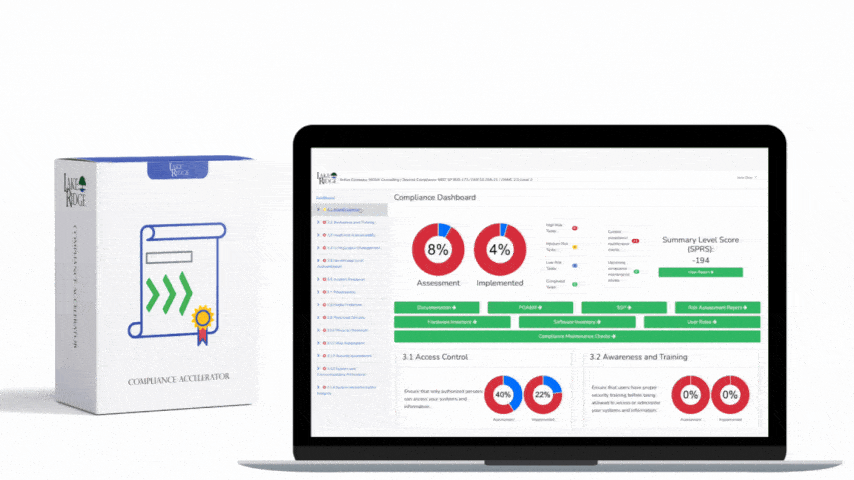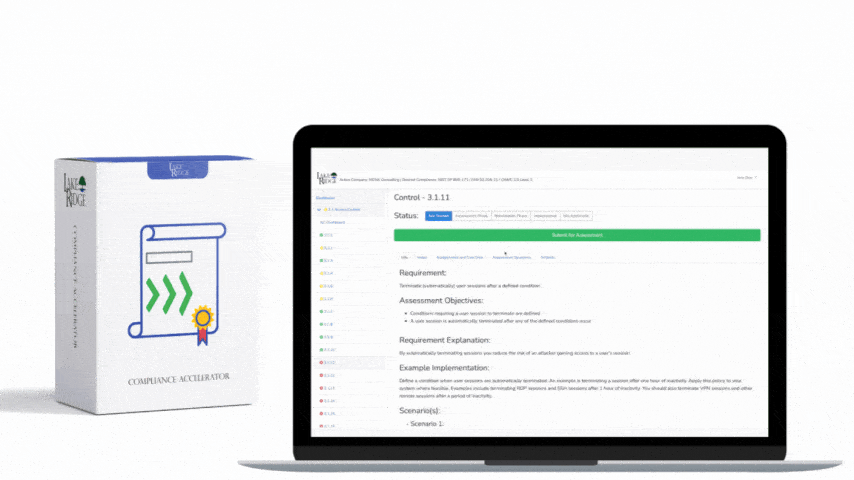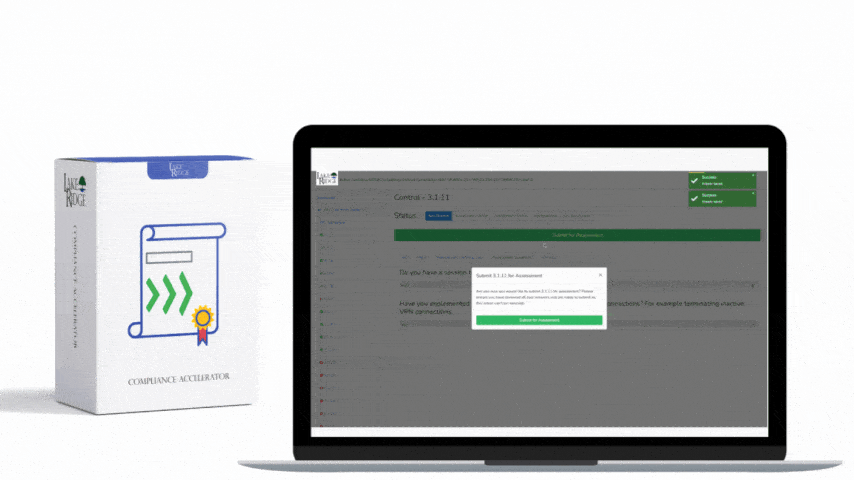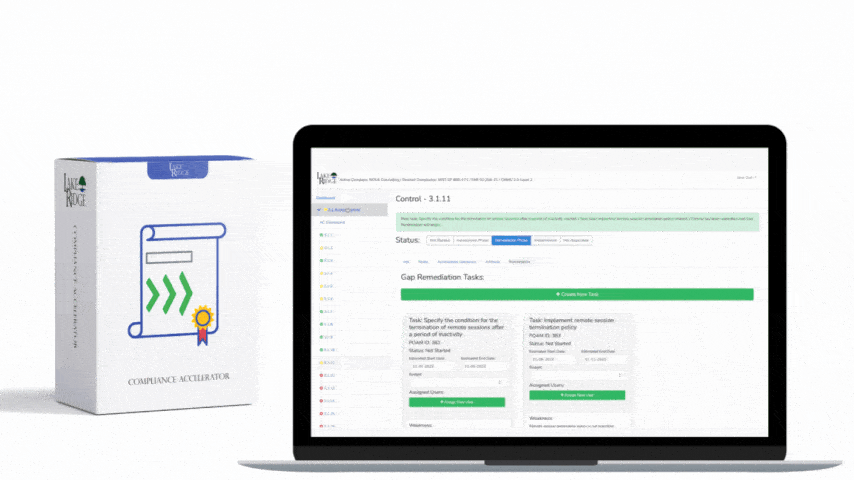
Requirement
NIST SP 800-171 REV.2 / CMMC 2.0 Level 2 - Control - SC.L2-3.13.16 – Protect the confidentiality of “Controlled Unclassified Information” (CUI) at rest.
Understanding the Requirement
This control requires that an organization ensure the confidentiality of Controlled Unclassified Information (CUI) when that data is stored and not actively moving across networks. CUI at rest includes files on desktops, laptops, servers, external drives, and mobile devices; the objective is to prevent unauthorized disclosure while data resides on these media. As part of NIST SP 800-171 REV.2 / CMMC 2.0 Level 2, you should adopt administrative policies and technical controls so stored CUI remains protected whether by encryption, physical access restrictions, or other compensating safeguards.
Technical Implementation
- Create and publish an "CUI at Rest" policy. Specify which data types are CUI, define where CUI may be stored, require approval for local storage, and mandate approved protection methods (e.g., full-disk encryption, encrypted containers, or locked storage). Include responsibilities and an exception process.
- Deploy full-disk encryption on endpoints and servers that can store CUI. Use native tools (BitLocker for Windows, FileVault for macOS) or centrally managed third-party solutions. Enforce encryption via configuration management or endpoint management so new machines are provisioned with encryption enabled.
- Encrypt removable media and backups. Require that all USB drives, external HDDs/SSDs, and laptop backups that may contain CUI use strong encryption (AES-256 or equivalent) and password-protected keys. Maintain a policy for encrypted backup rotation and secure offsite storage.
- Implement access controls and inventory management. Maintain an inventory of systems and media that are authorized to store CUI. Limit who can write CUI to local devices and use role-based access control so only necessary personnel can access CUI on a device.
- Manage keys and recovery securely. Use centralized key management or corporate recovery keys for full-disk encryption so devices are recoverable without weakening security. Protect recovery keys in a hardware security module (HSM) or an access-controlled secrets vault with logged access.
- Complement encryption with physical and procedural controls. For servers or backups stored onsite, use locked cabinets, controlled data center access, and chain-of-custody for removable media. Train staff on handling CUI and periodically audit encryption status and policy conformance.
Example in a Small or Medium Business
Acme Design Co., an SMB working on government contracts, identifies project documents and CAD files as CUI. The company updates its security policy to require encryption for any device or media that stores CUI and documents approved storage locations. The IT manager rolls out BitLocker to all Windows workstations and FileVault to Macs, using the company’s MDM to enforce encryption and collect recovery keys into a secure vault. External hard drives used for field work are provisioned as encrypted drives and tracked in an asset inventory; employees sign them out and log their use. Backups of CUI are encrypted before leaving the production environment, and an offsite backup vendor is contractually required to maintain encryption and access controls. Physical access to the server racks that host on-premise file shares is limited to two authorized administrators and controlled with badge access and logs. Finally, staff receive short training on what counts as CUI, how to store it, and who to contact when a device is lost; quarterly checks verify encryption status and inventory accuracy.
Summary
Combining a clear policy that defines CUI and approved storage methods with technical measures such as full-disk encryption, encrypted removable media, centralized key management, and inventory/access controls will meet SC.L2-3.13.16's goal of protecting CUI at rest. For SMBs, the pragmatic path is to standardize encryption on endpoints and servers, secure backups and removable media, enforce controls through MDM or endpoint management, and back those controls with physical protections and staff training—together these measures maintain confidentiality of stored CUI without undue operational burden.